Digital Audio Workstations, or DAWs, are software which combine the functionalities of multitrack recording, MIDI programming, and digital signal processing (DSP), making them the most comprehensive tools for how music is made in a variety of modern applications.
A Note on DAW-Specific Courses
Some Berklee Online courses are designed around specific DAWs, while in others, students can use the DAW of their choice. While all DAWs are powerful pieces of software that can accomplish the same tasks, there are some differences between them which make some more suited toward particular workflows over others. This article will describe highlights about each of the most common commercial DAW software, and provide suggestions of fitting applications for each.
Links to Berklee Online courses which require specific DAWs are included at the bottom of the information for each respective DAW below.
For courses not requiring usage of a specific DAW, students are encouraged to utilize the full version of the DAW which fits their personal workflow and goals. Many full-featured DAWs are also available with educational pricing, so keep an eye out for discounts especially for students. You can also check our Student Deals Page for more information about available education discounts.
Ableton Live
Ableton Live
Known for: A performance-based, looping, and sound-design-oriented workflow, great for preparing live DJ sets and for synthesizing electronic music.
Ableton Live is the DAW of choice for many pop and electronic producers, sound designers (such as for video games), and DJs when performing live sets.
Standout Features
- The user can switch between a Session View interface (where clips of audio or MIDI can be programmed as loops and launched during playback/recording) and Arrangement View (in which audio and MIDI clips display laid out on a timeline).
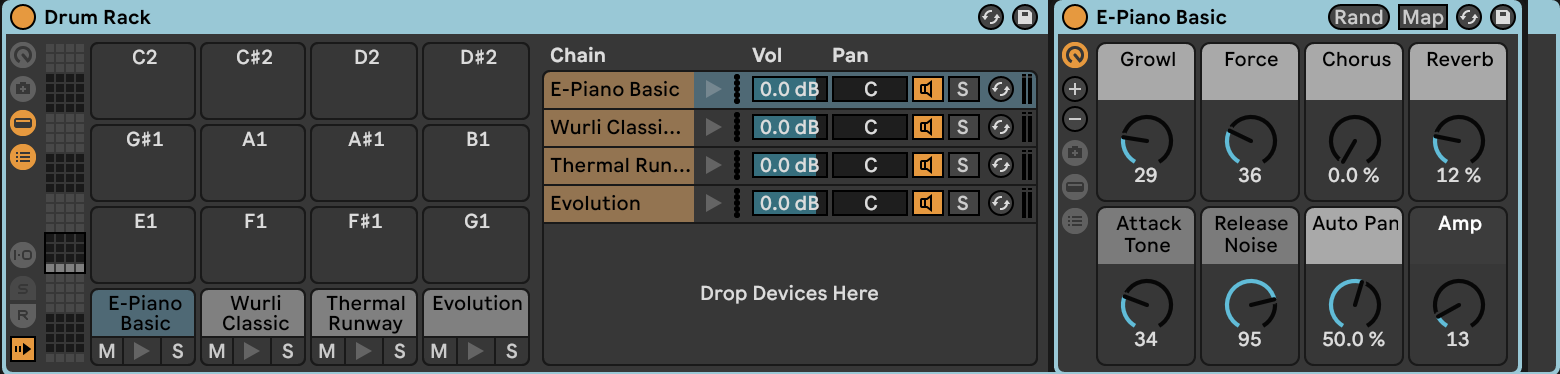
- Ableton features a unique Rack setup for software instruments and plug-ins, which is ideal for a workflow oriented around sound design. Racks are highly modular and can even host multiple instruments or effects at a time for ease of control.
- MIDI programming is very intuitive in Ableton; with the press of a button, Ableton Live's interface can be set to MIDI Map Mode. In this mode, parameters on a MIDI controller can be programmed by simply clicking them in Ableton, then adjusting the desired controls on the hardware itself. See our article about MIDI Controller Setup and Mapping in Ableton Live here .
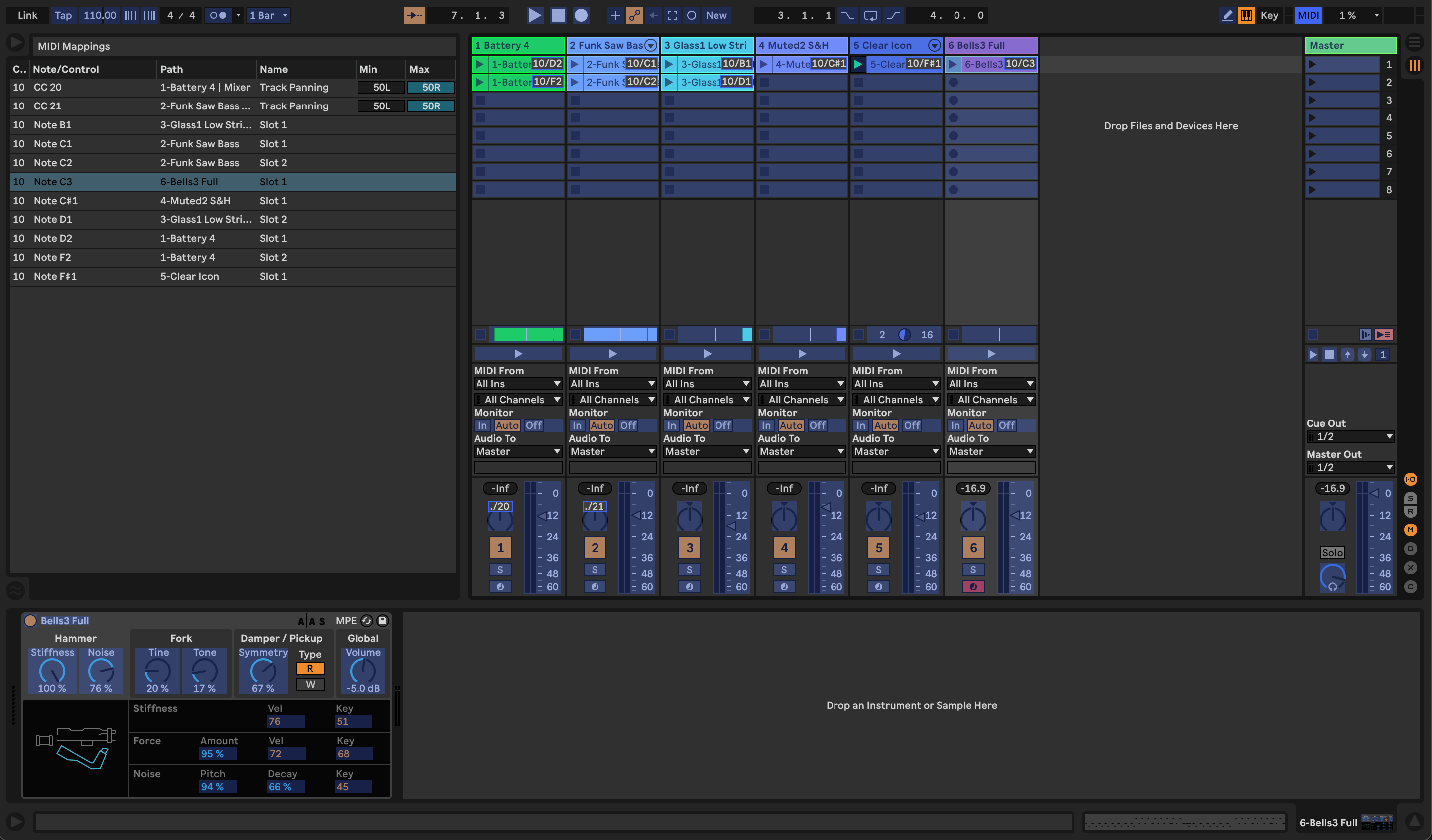
-
Some MIDI controllers, such as the Akai Professional APC40 mkII and Novation Launchpad, were co-developed with Ableton and integrate more intuitively than others.
- The Push is another MIDI controller developed by Ableton for optimal integration with Ableton Live.
- Ableton has a variety of algorithms for its Warp feature, used to process audio and speed it up, slow it down, and/or change its pitch––ideal for DSP applications such as producing remixes, mashups, or transitions between songs and sets.
Considerations
- Audio routing, and especially gain-staging, can become complicated if not properly managed.
- Generally not ideal for rigorous audio editing (e.g. post-production work), especially involving video.
Student Discount
Educational pricing is available for Berklee Online students via the Student Deals Page.
Berklee Online Courses Specializing in Ableton Live
Logic Pro
Logic Pro
Known for: Production and mixing capabilities with a timeline-oriented workflow and a user-friendly interface.
Logic is a popular choice for users who utilize both MIDI and audio to an equal extent, such as composers when sequencing orchestral libraries alongside other virtual instruments and audio recordings.
Standout Features
- The user interface focuses around the project's timeline view with simple key-commands available to bring up additional panels and menus.
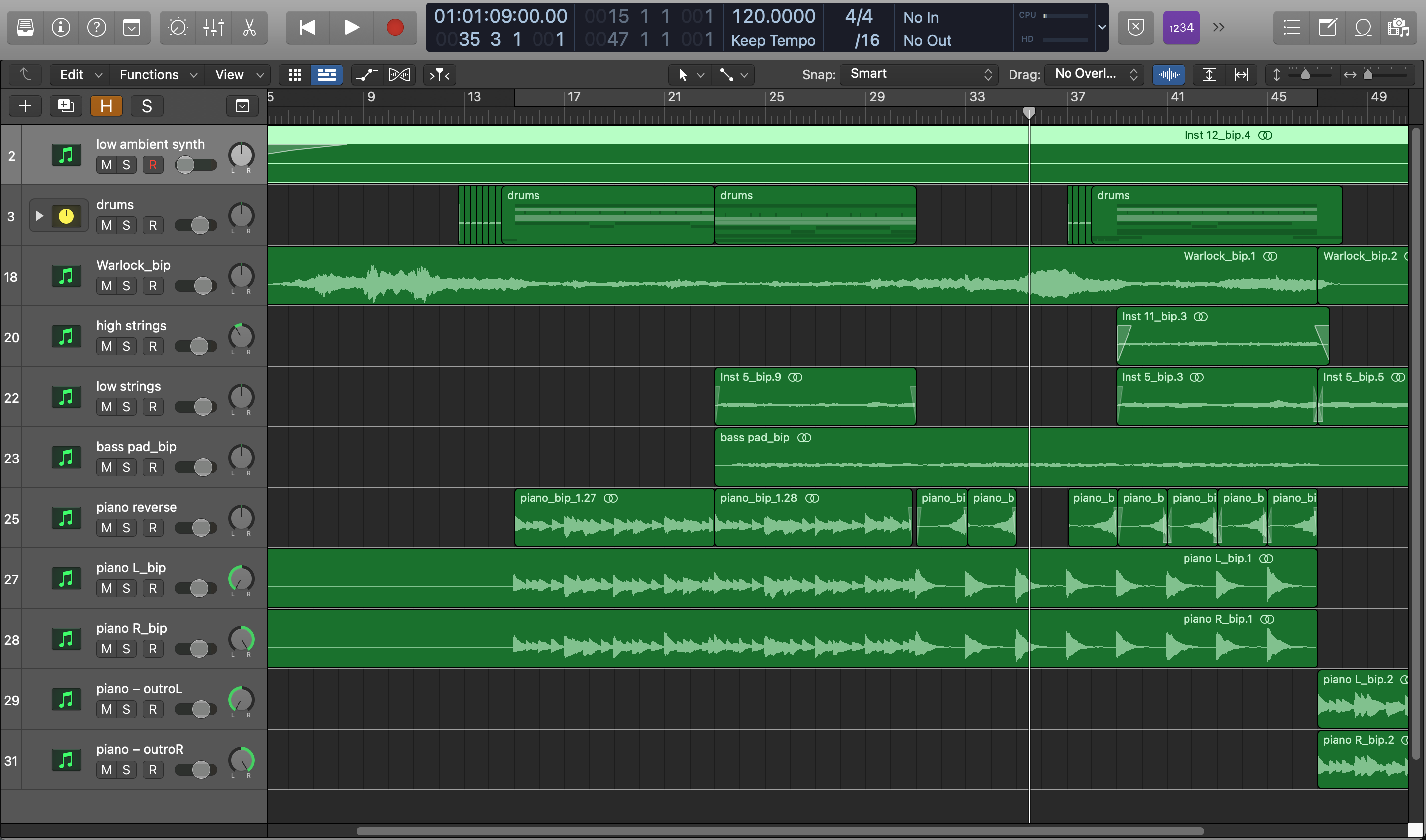
- The user can quickly create snapshots of the screen layout (Screensets) to customize the view of the interface. You can also save Project Alternatives, or copies of the project at various stages, to more easily switch between different iterations of your work.
- Logic automatically detects hardware changes and switches the software's playback device when any changes are made (e.g. if you were to plug in headphones instead of using speakers, etc.); compared to other DAWs which often require a manual change in Preferences and/or restart to initialize changes.
- Both audio and MIDI tracks are straightforward to record, input, and edit. The Bounce-in-Place feature is also great for quickly printing MIDI sequences onto parallel audio tracks to then edit them in different ways.
- CPU is optimized to simultaneously handle a large amount of virtual instruments and additional plug-ins for ease of sequencing.
- Includes a robust suite of plug-ins, instruments, and library content.
- Due to a similar user-interface and overlapping library content, Logic Pro can be a great upgrade for users of GarageBand looking to take advantage of a DAW's more advanced capabilities.
- A special mobile version is also available for iPadOS, but does not come with with all the features included in the desktop version.
Considerations
- Only available on Apple devices.
- Audio routing can be a little “too smart"; that is, can create a mess of gain-staging if proper attention is not paid in the mixer.
- File management is less straightforward outside of the program itself. By default, Logic sessions are saved as Package file types, and must be saved in folders for an easier time locating and managing the contained files.
Student Discount
A bundle of Apple software, including Logic Pro, is available for degree students via Apple's Education Store (only offered for students based in the US).
Berklee Online Courses Specializing in Logic Pro
Pro Tools
Pro Tools
Known for: The “industry standard” for studio recording, audio editing and mixing, as well as post-production.
Standout Features
- The user interface features a timeline-based Edit window with a separate Mix window for an easy back-and-forth workflow.

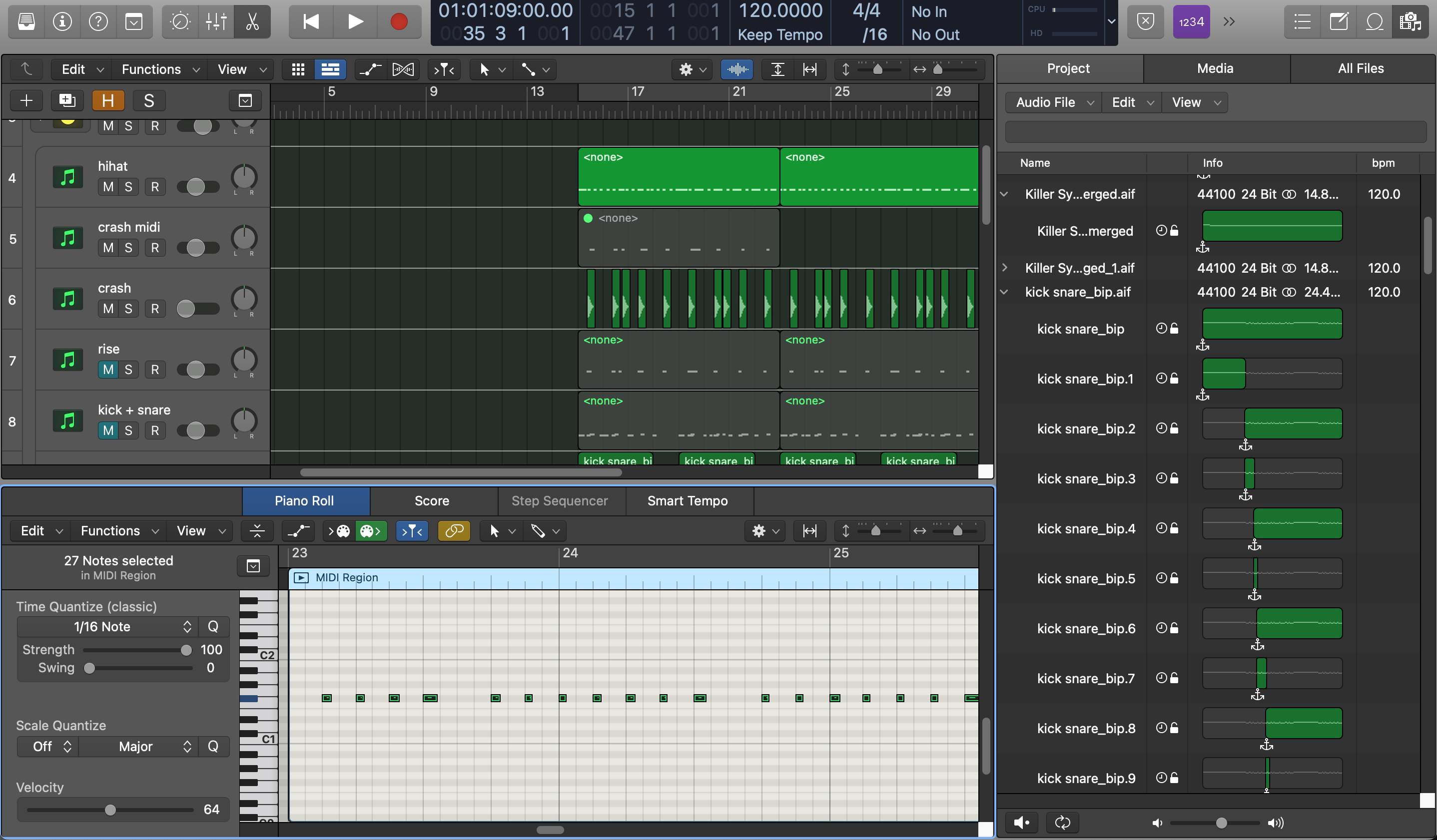
- Tools for optimized audio editing include:
- AudioSuite: a function for making immediate edits to clips of audio using plugins
- Beat Detective: an intuitive tool to detect transients within clips of audio and produce data points from them, which can then be used to generate a tempo map or conform clips to a grid
- Hundreds of advanced keyboard shortcuts which exponentially speed up the audio-editing process, although it does take time to become fluent in using them
- In Pro Tools, access to track input and output settings is available in multiple places, making it easy to adjust routing via the bus network, auxiliary tracks, routing folders, and so forth. This is ideal for complex projects with a high track-count, as well as for utilization in recording studios alongside a recording console.
Considerations
- MIDI input and programming can be cumbersome.
- Requires consistent management of playback engine settings, CPU/RAM usage, and file management for individual projects.
- Takes practice and extensive familiarization with keyboard-shortcuts to most efficiently and effectively use the program.
Student Discount
Available for Berklee Online students via the Student Deals Page through Avid.
Berklee Online Courses Specializing in Pro Tools
Cubase
Cubase
Known for: Fluid audio-recording and MIDI-programming interfaces; highly-streamlined MIDI integration with virtual instruments.
Cubase has been becoming more popular for producers and film composers due to its well-roundedness in handling all of audio, MIDI, and video, and most especially for its optimized integration with virtual instruments.
Standout Features
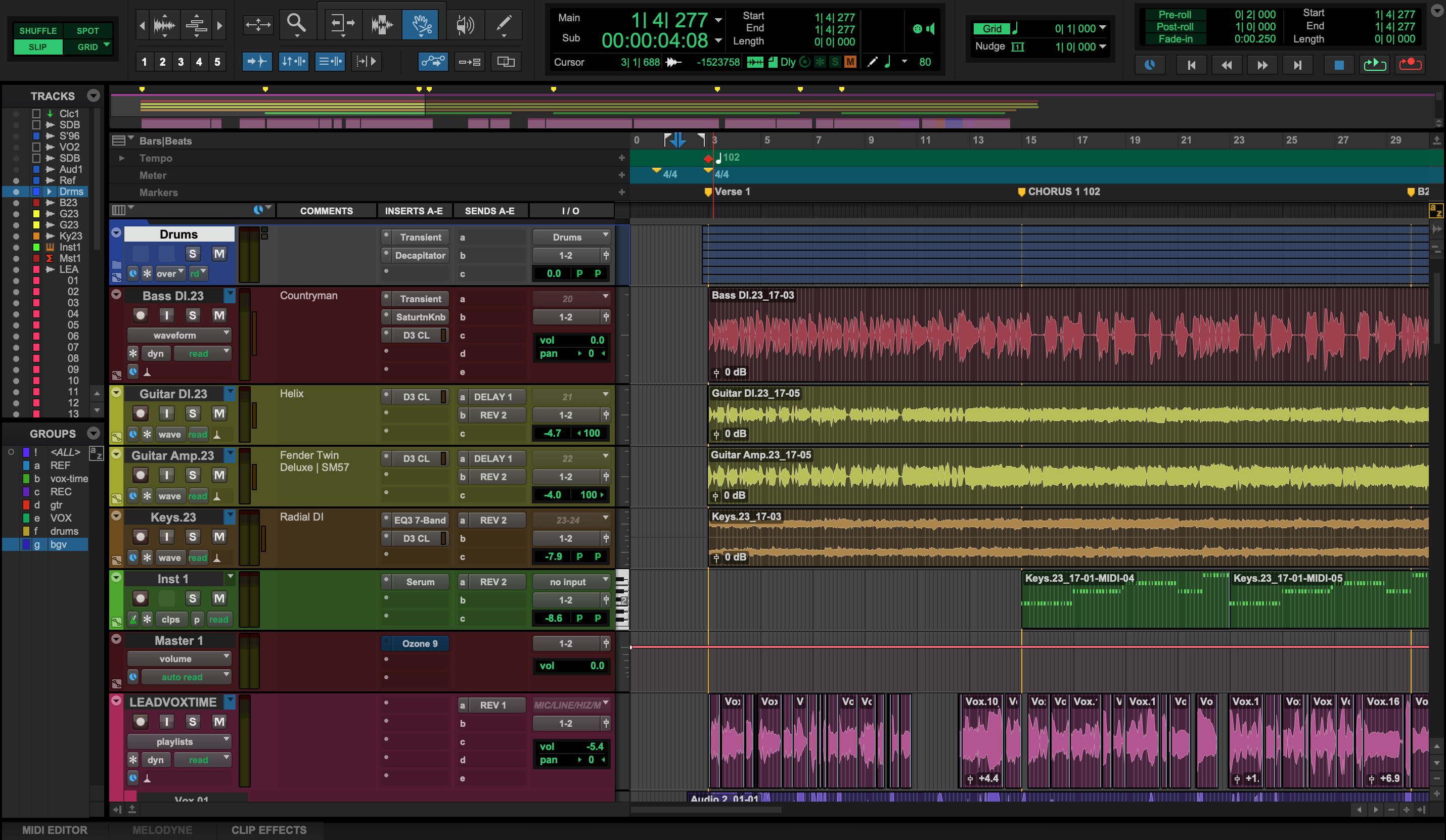
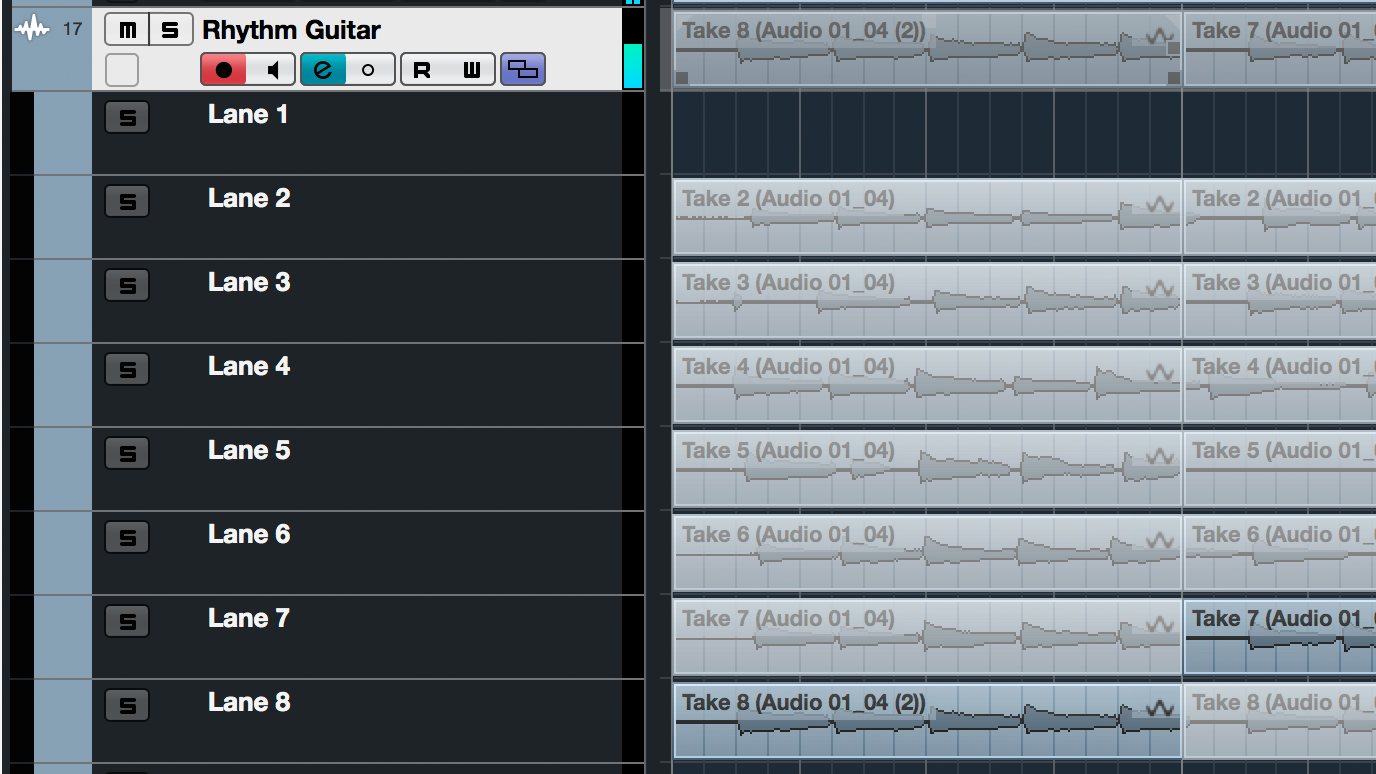
- Both audio and MIDI tracks are straightforward to input and edit. Cubase's Comping feature makes for fluid compiling of multiple takes of audio tracks, and its Audio Warp Quantize allows for quick DSP on multiple audio tracks at a time.
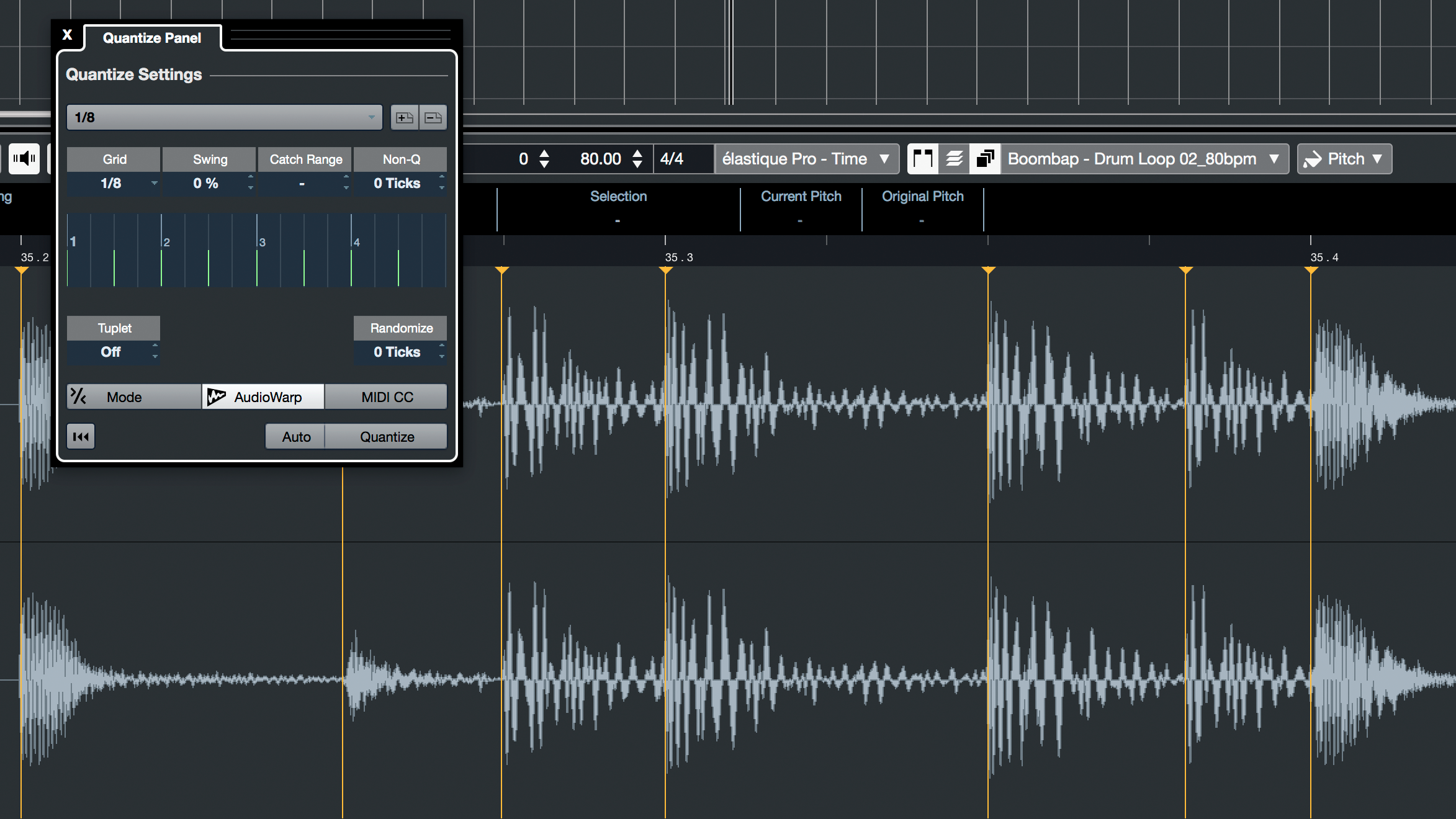
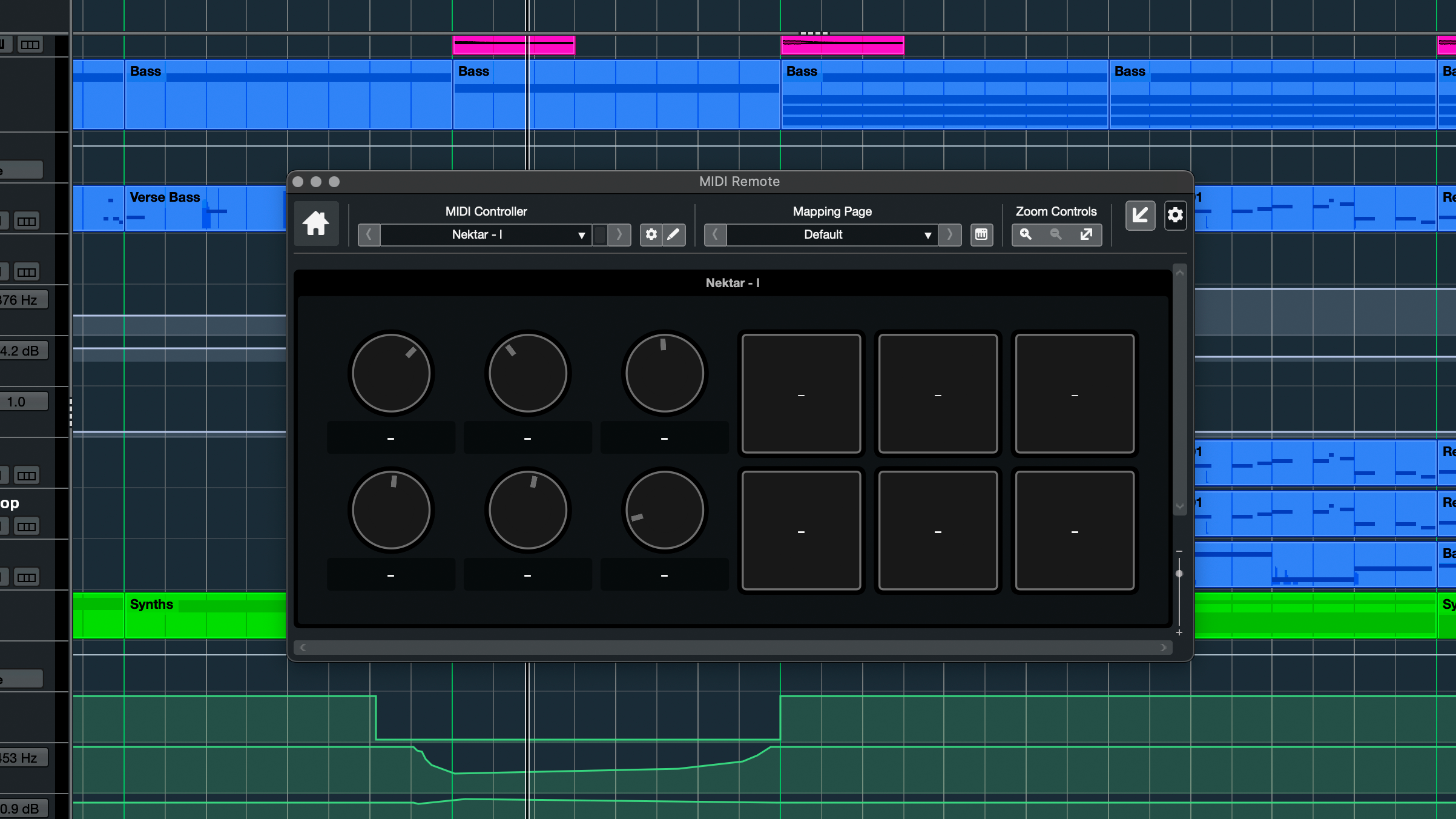
- MIDI input, programming, and mapping is intuitive to assign and control, especially using Cubase's MIDI Remote feature, which detects the user's MIDI device and allows for quick parameter assignments. Even without a hardware MIDI controller, this function also provides a quick and intuitive way for automating plugin parameters.
- Cubase has highly-customizable options for track views as well as channel batch-exporting.
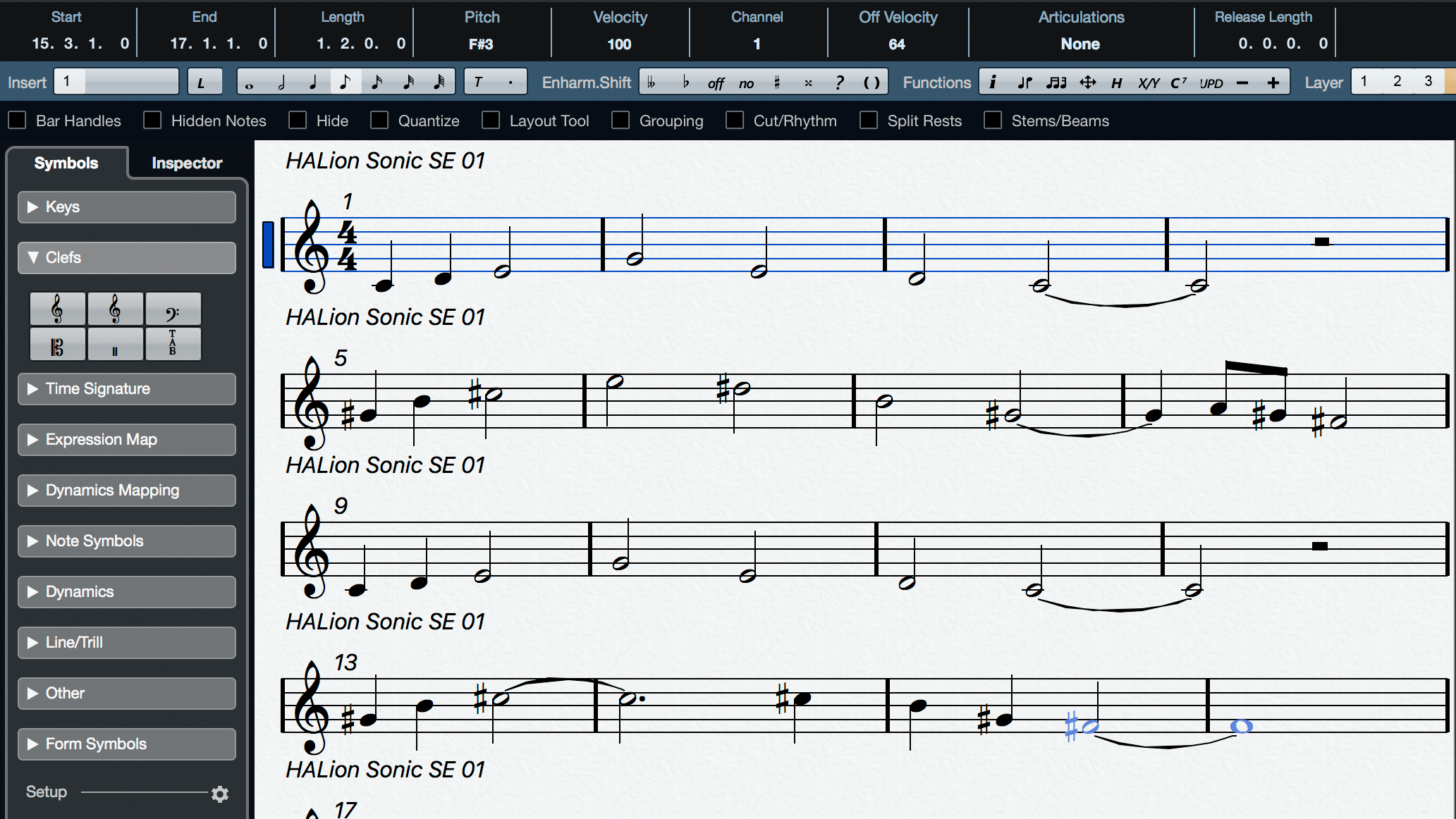
- Cubase also features a built-in Score Editor for music notation, notable for supporting more notation methods than other DAWs including advanced symbols, lyrics, and comments. This makes the DAW a popular choice for composers who frequently convert their own work into notation.
Considerations
- Some documentation may be outdated and appear different from current versions.
- There is a steep learning curve to becoming familiar with the program's unique layout and keyboard shortcuts, as well as setting up more advanced audio routing.
- Cubase can take up a lot of space, so management of system resources (CPU and RAM) is important to consider.
Student Discount
Available for Berklee Online students via the Student Deals Page.
Berklee Online Courses Specializing in Cubase
FL Studio
FL Studio
Known for: User-friendly and quickly-accessible interface.
FL Studio is the DAW-of-choice for many “bedroom-producers” in the current scene, primarily due to its fast-paced workflow and massive selection of samples, which make for quick beat-production and creation of song sketches on the fly.
Standout Features
- FL Studio comes with a large sample selection and an intuitive interface with instrumental loops and drum samples ideal for beat-making.
- Along with loops and samples, FL Studio also includes a variety of high-quality processing plug-ins and virtual instruments.
- File management in FL Studio is straightforward when saving projects and exporting to other formats (MP3, WAV, etc.).
- Extensive documentation for FL Studio, along with active online communities of the DAW's user-base, allow for users to quickly troubleshoot issues and share knowledge.
Considerations
- Audio recording can be confusing at first, and sometimes is a hassle in terms of CPU management.
- Some processes, such as audio editing, are made to be easy to use, but in turn lack some advanced functionality which is standard to other DAWs.
- Auto-saving feature is slower than some other DAWs, so work can be lost if not frequently saved.
Student Discount
Available via a distributor local to the user, on which information can be found on Image Line's Educational and Academic Licenses page.
GarageBand
GarageBand
Known for: A beginner-friendly user interface available for free on Apple devices.
GarageBand is known for being a great introductory option into the world of music production, and is also frequently used by songwriters who want to create their own song demos rather than relying on others to put down their ideas.
Standout Features
- GarageBand's user interface is very user-friendly, featuring intuitive key-commands and a clear layout. It also shares many commonalities with Logic Pro, making it a great gateway into a more advanced DAW.
- GarageBand comes with a large library of loops and samples, ideal for usage in a song's pre-production phase.
- A special mobile version is also available for both iOS and iPadOS, a notable mention for Apple's effort to push the boundaries of music production on-the-go. However, it does not come with all of the features included in the desktop version.
Considerations
- Only available on Apple devices.
- Some features meant to be convenient, such as the automatic addition of effects on certain track types, can interfere with the user's workflow.
Cakewalk by BandLab
Cakewalk by BandLab
Known for: A free, beginner-friendly option allowing usage of robust included plug-ins, along with more advanced MIDI- and audio-editing capabilities.
Cakewalk is considered by many to be an equivalent option to GarageBand—just for Windows users instead of Mac—due to its ease of use, making it a great choice for beginners.
Standout Features
- Cakewalk by BandLab (formerly called SONAR) is a free full-featured DAW, bringing a clean user interface to users of Windows OS.
- Cakewalk is thoroughly documented with extensive tutorial videos, articles, and forums available for users seeking more resources and a community for learning music production.
- BandLab's proprietary software VocalSync® is included as a plug-in within Cakewalk, and is a powerful tool comparable to other vocal-alignment software.

- In addition to VocalSync, Cakewalk also comes with all the basic tools needed for fundamental audio editing, including its own compressor, EQ, reverbs and delays, etc.
- Cakewalk is also compatible with touchscreen devices that run Windows OS, such as the Microsoft Surface and Lenovo Flex.
Considerations
- Only available for users of Microsoft Windows OS on desktop.
- While Cakewalk does auto-save projects by default, it is recommended to increase the auto-save frequency (easily done in the software's settings) or manually save projects frequently.
- Usage of third-party virtual instruments, loops, and samples is recommended, as Cakewalk is a lightweight software and doesn't come with as robust of a library.
REAPER
REAPER
Known for: Inexpensive, efficient, highly customizable, and user-friendly.
REAPER is a great introduction to a full-featured DAW since it can be downloaded and used for a free 60 days before the user has to pay. It is frequently used by those just getting into music production. If you require all the functionality of a full-featured DAW on a basic level, then REAPER will get the job done.
Standout Features
- REAPER is highly versatile in its compatibility with different systems (e.g. OS versions, digital formats, etc.) and hardware peripherals (e.g. MIDI controllers).
- The software features powerful audio- and MIDI-editing capabilities, and more advanced users will find routing (including multichannel) to be intuitive.
- REAPER's user interface is customizable, with several skin themes available online that the user can install and use to feel more at-home. Scripting and extensibility also make the software more versatile for a variety of specializations.
- The DAW comes with hundreds of effects for both audio and MIDI, and includes built-in DSP functions.
Considerations
- REAPER's “discounted” license suits most of its user-base, but commercial usage falls under certain terms and conditions (see the REAPER purchase page for details on the different licenses available).
Reason
Reason
Known for: Versatile instruments; Reason Rack plugin version for utilizing within other DAWs.
Standout Features
- The user interface features a Rack view where the user can add various instruments and adjust their signal flow, along with a Sequencer view where MIDI and audio clips can be arranged on the session timeline.
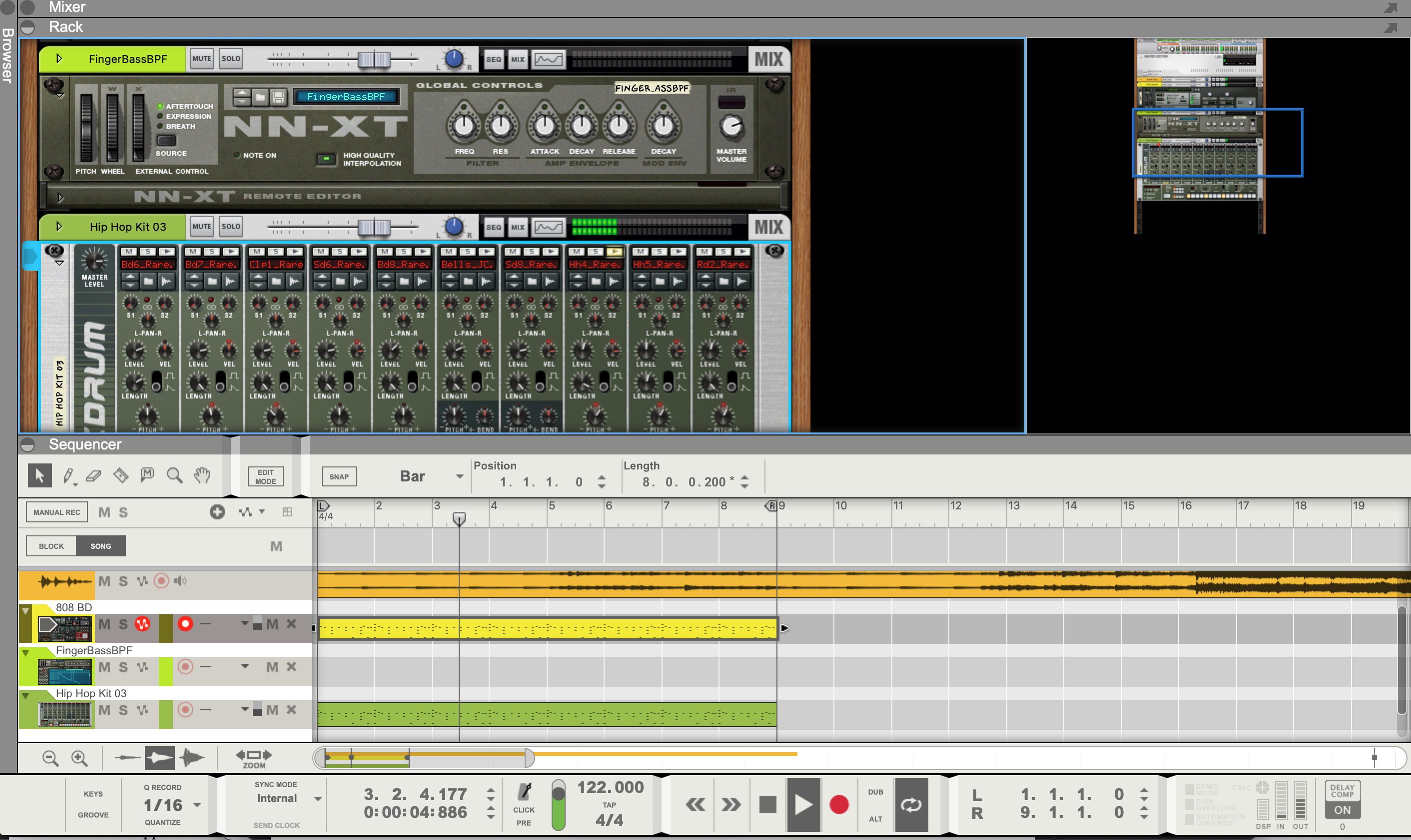
- Reason also comes with the Reason Rack Plugin for instantiating within other DAWs to then have access to Reason's collection of virtual instruments outside of the program alone.
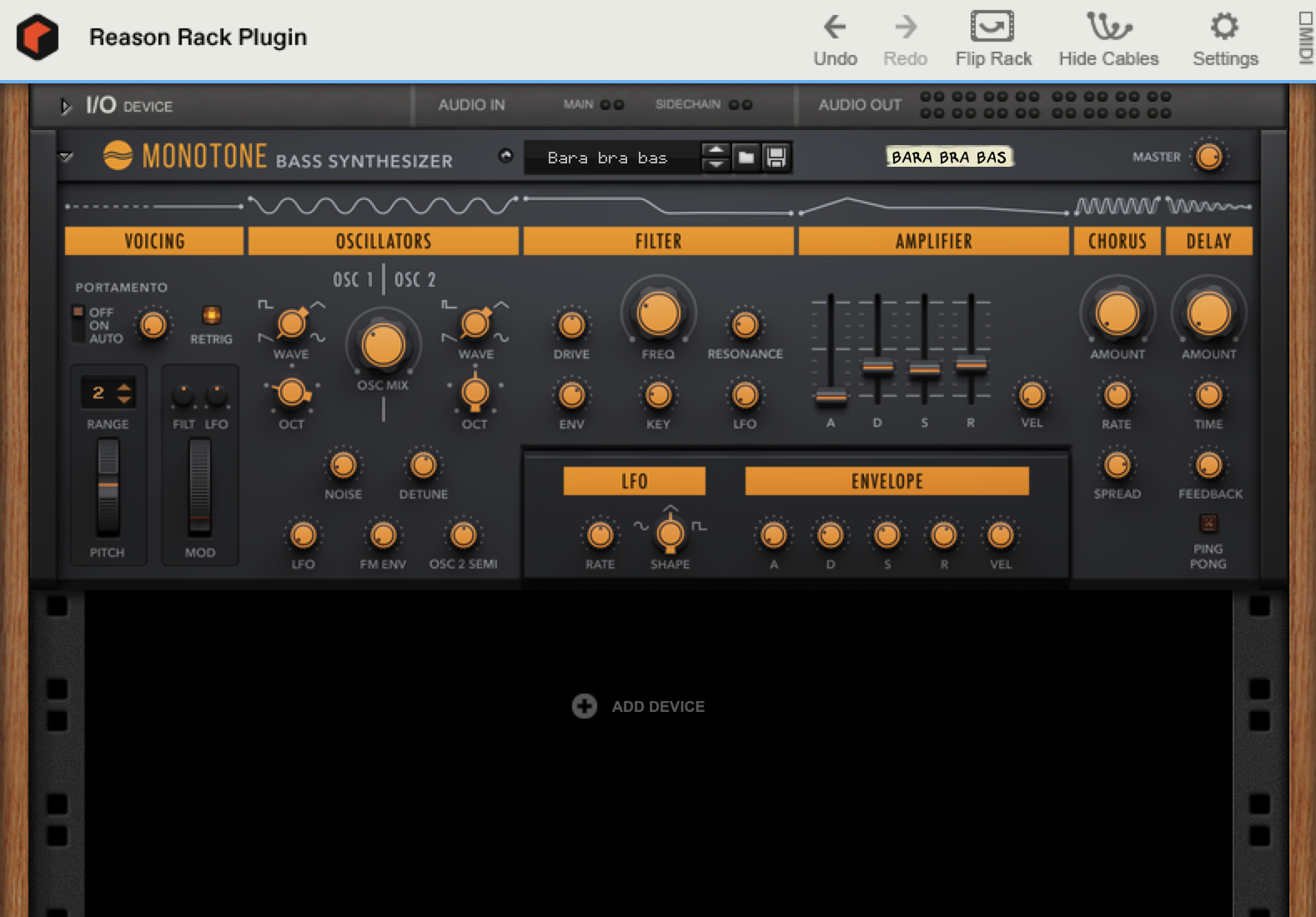
Considerations
- Audio is cumbersome to handle in Reason, and for this reason, most users exclusively utilize the software for its MIDI-sequencing capabilities and included software instruments.
Student Discount
Exclusive deal available for Berklee Online students via the Student Deals Page.
Berklee Online Courses Specializing in Reason
Digital Performer
Digital Performer
Known for: High level of customization; common usage for film scoring and sequencing.
Digital Performer exhibits a more “niche” user-base of composers for film, beat programmers, and producers due to its highly-customizable interface, which is great for composing music using virtual instruments.
Standout Features
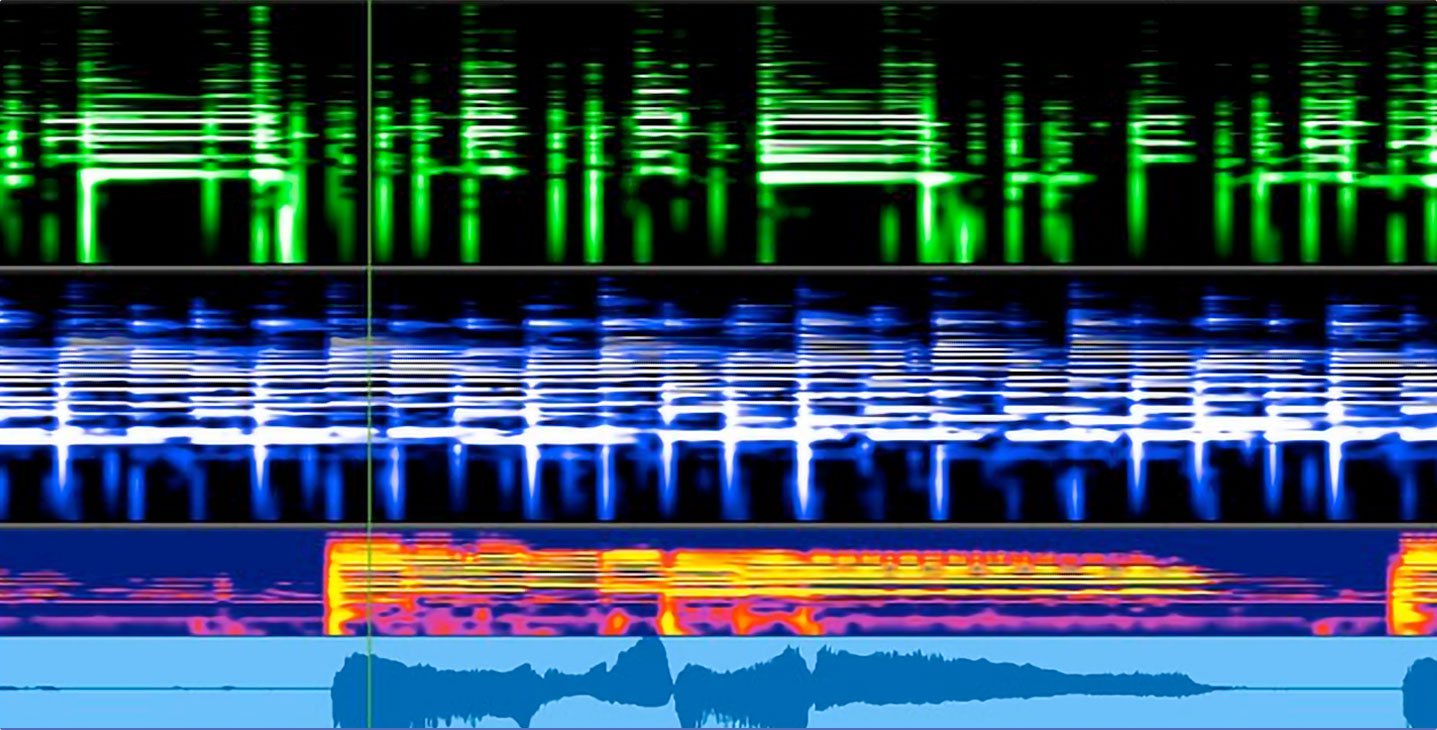
- Digital Performer features a variety of views and displays to choose from, such as a spectral display for audio tracks (in addition to the standard waveform-view).
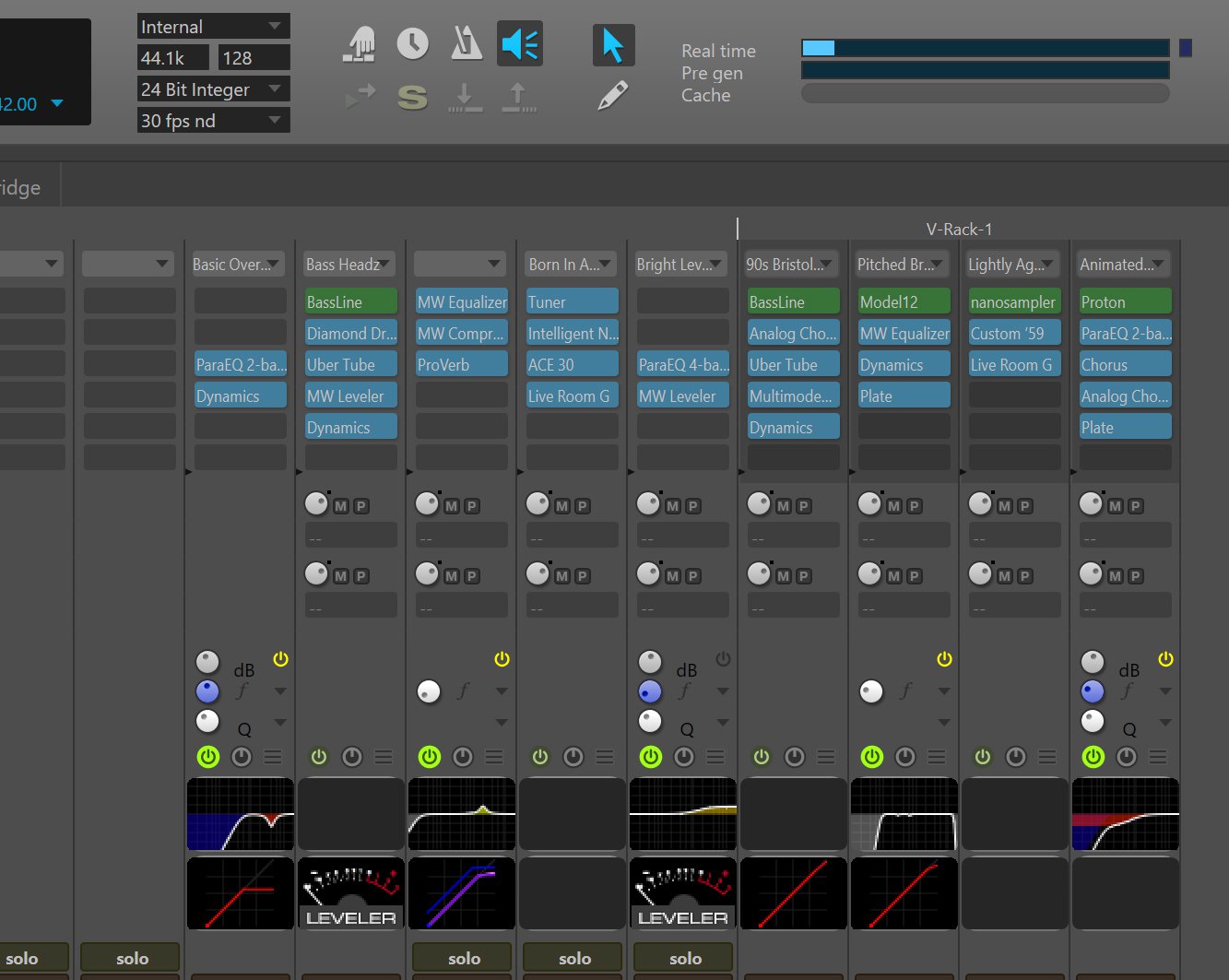
- V-Racks save on CPU processing by loading virtual instruments and plugins in one place for individual sequences to then access (as opposed to creating multiple instances of a plugin for each sequence).
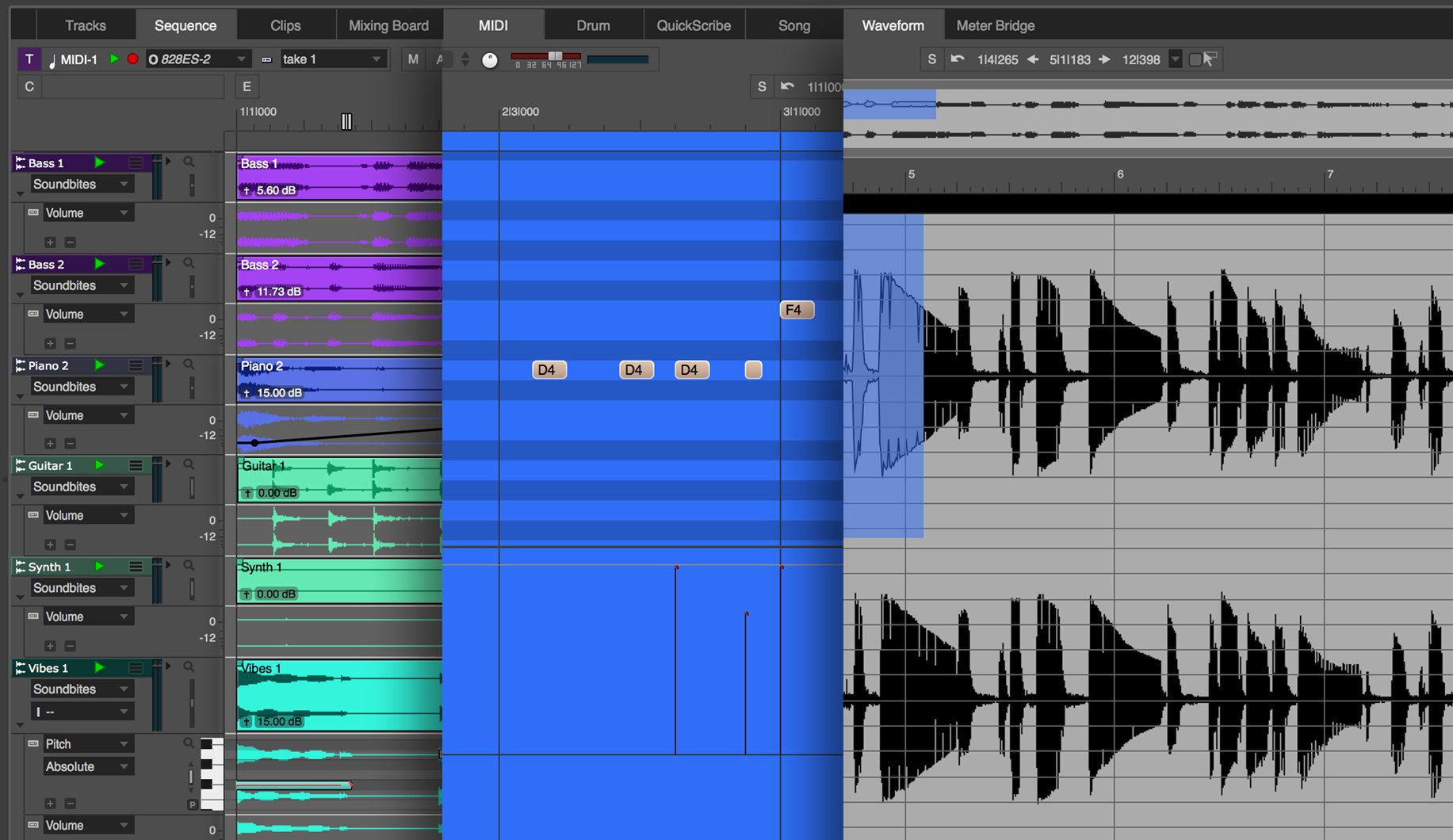
- Digital Performer exhibits a robust MIDI editor, as well as a highly-rated built-in pitch correction tool in its Waveform editor.
- Digital Performer is, as per its title, an excellent tool for live performance, once again due to its high customizability and modular interface.
Considerations
- Using third-party sample libraries is recommended; while Digital Performer does include a large collection of virtual instruments itself, some consider the selection lackluster compared to other options.
- The user interface can be complex to grasp at first, and the program uses different terminology from what is often standard (e.g. “sequences,” “V-Racks,” etc.).
Recommendations for Usage Scenarios
Below are some possible usage cases and recommendations of which DAW might best suit each.
- Studio recording, audio editing, mixing: Pro Tools
- Composing for film: Cubase, Logic Pro, Digital Performer
- Audio post-production: Pro Tools
- Pre-production for beat-making, sound design: Ableton Live, FL Studio, Cakewalk by BandLab
- Pre-production for songwriting, producing demos: GarageBand, REAPER, Cakewalk by BandLab
- Sequencing, MIDI programming: Ableton Live, Reason, Digital Performer
- Live performance: Ableton Live, Digital Performer

